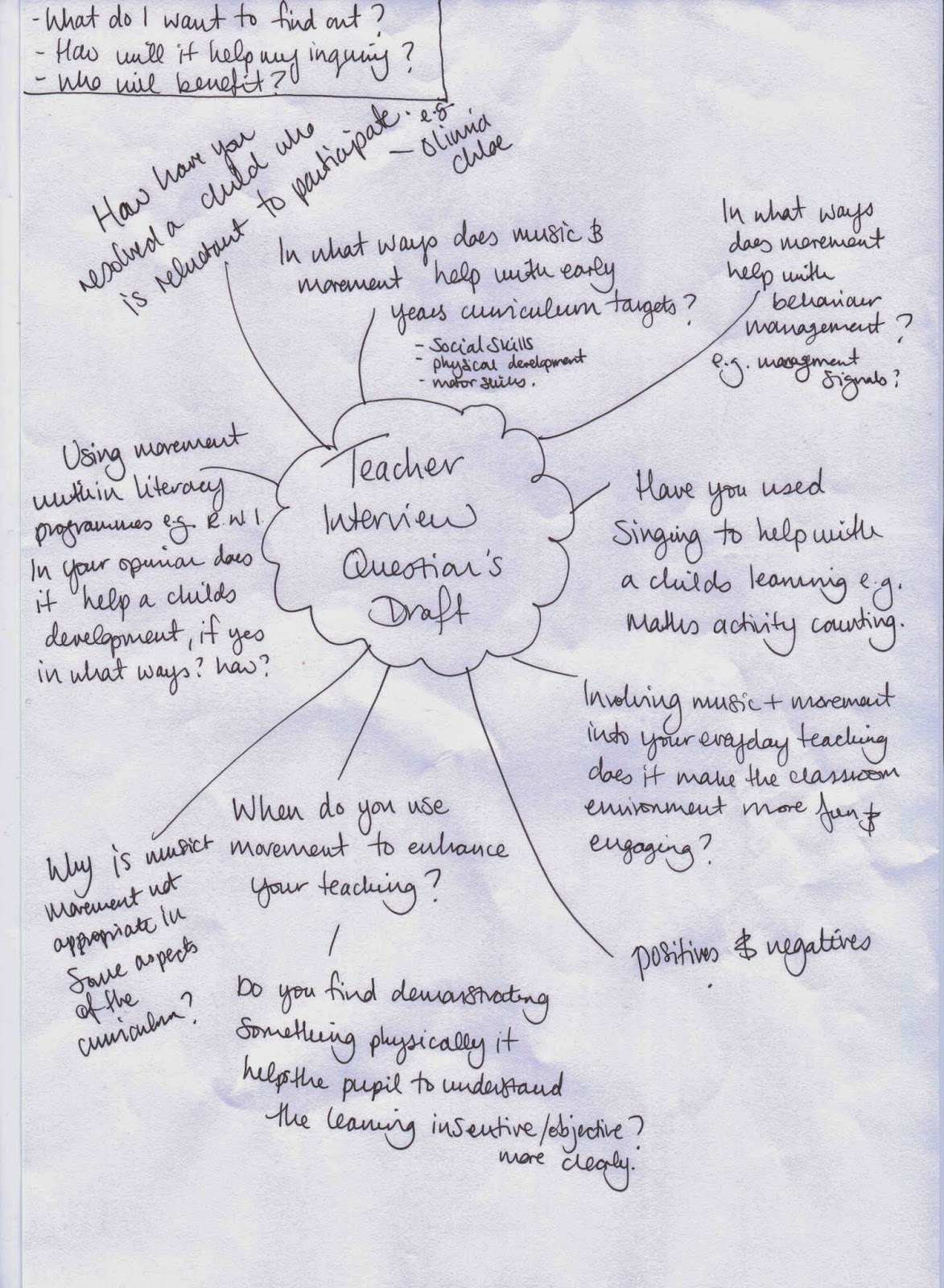
Being
an early years practitioner I have experience and knowledge of the early years
curriculum and how music and movement is used in everyday classroom scenarios.
However, I wanted to find out what evidence is available in proving that it helps
early years development.
A
piece of literature that stood out to me is:
‘Bringing the Froebel approach to your
early years practice’
by
Helen Tovey (2012)
Helen
Tovey discusses how ‘Froebel’ encouraged mothers to use finger rhymes and songs
to stimulate their childs development:
‘Froebel devised a
series of some fifty finger rhymes, action songs and games for mothers and
other family members to share with babies and younger children at home. These
were published as ‘Mother Songs’…illustrations included sketches to show the
appropriate finger and hand movements for the song.’
‘Froebel argued that
these were not just trivial amusements to occupy babies but provided key
learning together at home as of central importance in his educational
approach.’
He explained the
positive effect of finger rhymes:
- ‘Close
intimate relationship between mother and child as they shared finger
rhymes e.g. child sitting on mother’s lap.’
- ‘Infants
were actively involved through moving their limbs. The finger rhymes
focused attention on hands and fingers in particular and helped to
strengthen them. The action songs and ring games focused on developing
whole-body movements and coordinating movement with others. Froebel argued
movement and mind are inextricably linked.’
- ‘Developing awareness of symbols.
The finger rhymes are important in developing children’s awareness of
symbolic representation. Fingers, movements or sounds can stand for something
else….Gaining fluency in the use of symbols is vital for communicating
through a range of symbolic languages such as music, dance, drawing and
painting, as well as spoken and written languages.’
Helen Tovey ‘Bringing
the Froebel approach to your early years practice’.2012.
Below
Helen Tovey expresses how ‘Froebel’s theories were ahead of the times and
revolutionary. She points out they are similar to modern methods we use today
in early years development practice.
‘Froebel’s
ideas were way ahead of his time. The idea that mothers were key educators of
their children, and that pictures, songs and rhymes enjoyed in a warm, loving
relationship on mother’s laps were important educational tools for babies and
small children must have been considered revolutionary in the culture and
context in which Froebel lived.’
Helen
Tovey (2012) Bringing the Froebel approach to your early years practice’
Within
my inquiry I wanted to find out if music and movement helps a childs
development, Helen Tovey points out that rhyming skills can develop reading
skills. Also by using finger and nursery rhymes with movement it develops musicality
and sense of ‘beat’:
‘Young
children’s awareness of rhyme is a powerful predictor of later success in
reading. As research by Goswami has shown, children who have good rhyming
skills are much better at making analogies and become better readers than
children who have poor rhyming skills (cited in Whitehead 2007).’
Helen
Tovey (2012) Bringing the Froebel approach to your early years practice’
‘The
rhymes and rhythms of many of the traditional finger and nursery rhymes,
accompanied by actions of hand clapping, finger tapping, body swaying, or foot
stamping, develop an awareness of ‘beat’ and love for the musicality of
language which is crucial for the enjoyment of poetry, literature, music and
drama.’
Helen
Tovey (2012) Bringing the Froebel approach to your early years practice’
Helen
Tovey also uses a neuroscientist point of view to conclude her findings; she
links the importance of movement and music with circuitry of the brain. This
scientific point of view argues that music and movement can stimulate the brain
to develop other areas of progress e.g. motor skills.
‘Evidence
from neuroscience shows the importance of movement, music and dance in building
the circuitry of the brain. Finger rhymes and movement games help motor
development, and stimulate the senses of balance and space, all of which are
needed for such things as reading, writing, riding a bike, and so on
(Goddard-Blyth 2011).’
‘As well as the strong links with literacy,
many finger rhymes, action songs and ring games can develop language associated
with simple counting- for example, ‘1,2,345, once I caught a fish alive’, or
with counting and taking away e.g. ‘Five currant buns’…other songs concentrate
on spacial concepts such as up, down, round, in, out, under, far away, and so
on….All of these spatial concepts are linked with movements. Mathematical
concepts can therefore be emphasised in a meaningful context.’
Helen
Tovey (2012) Bringing the Froebel approach to your
early years practice’
Helen
Tovey also points out that music and movement can help social interaction with
other people and by using a singing voice in class can be more effective in
getting pupils attention than a using a speaking voice.
‘Singing, as Froebel
emphasised, creates joyfulness, group cohesion and a sense of community. It can
be an important way of reinforcing everyday events and routines, reflecting on
things that have happened and calming distressed or anxious children. Regular
songs connected with significant routines and times of the day, such as
greeting and partying songs are important ways of creating a regular rhythm to
the day.’
‘A
singing voice attracts children’s attention far more easily than a normal voice
and it is often easier to get things done accompanied by a song e.g. ‘this is
the way we pick up the blocks, pick up the blocks…’
Helen
Tovey (2012) Bringing the Froebel approach to your early years practice’
As
well as book literature I’ve looked at evidence via online sources, an article
that provides research evidence is an Article from:
Early
childhood news. Professional resource for teachers and parents
‘Linking
Literacy and Movement’
By
Rae Pica, Movement Specialist
Rae
Pica a movement specialist looks at the argument why learning through movement
is beneficial for a child’s development and that ‘movement is children’s
preferred mode of learning –and that children learn best through active
involvement’. The article approach is from a movement specialist point of view
and emphasises;
‘Children
need to physically experience concepts in order to truly grasp them.’
Below
is the article:
The
Argument for Learning through Movement
By Rae
Pico
Research
shows that movement is the young child’s preferred mode of learning – and that
children learn best through active involvement. For example, prepositions
– those little words so critical to language and life – are very much a part of
movement experiences. As children move
over, under, around, through, beside, and near objects (e.g., under the slide, through the tunnel, over
the balance beam), these words take on greater meaning to them. Olds (1994, p.
33) contends that such spatial orientation is also necessary for letter
identification and the orientation of symbols on a page. She writes: “The only
difference between a small ‘b’ and a small ‘d,’ for example, both of which are
composed of a line and a circle, depends upon orientation, i.e., which side of
the circle the line is on.”
When children
speak and listen to one another, as when they invent games on the playground,
they’re using and expanding their vocabularies and learning important lessons
in communication. When they invent rules for those games (as preschoolers like
to do), they further enhance their communication skills.
When children
perform a “slow walk” or “skip lightly,” adjectives and adverbs become much
more than abstract concepts. When they are given the opportunity to physically demonstrate
such action words as stomp, pounce, stalk, or slither – or
descriptive words like smooth, strong, gentle, or enormous – word
comprehension is immediate and long-lasting. Even suffixes take on greater
relevance when children act out the difference between scared and scary.
In all of these instances, the children have heard the word and both felt and
seen the meaning. And research tells us that the more senses used in the
learning process, the higher the percentage of retention (Fauth, 1990).
Jensen (2001)
labels this kind of hands-on learning implicit – like learning to ride a
bike. At the opposite end of the
spectrum is explicit learning – like being told the capital of
Peru. He asks, if you hadn’t ridden a
bike in five years, would you still be able to do it? And if you hadn’t heard the capital of Peru
for five years, would you still remember what it was?
Extrinsic
learning may be quicker than learning through physical experiences, but the
latter has greater meaning for children and stays with them longer. There are
many reasons for this, including the fact that intrinsic learning creates more
neural networks in the brain (Jensen, 2001). Another reason may be that it’s
simply more fun!
Carla
Hannaford (1995) writes: “We have spent years and resources struggling to teach
people to learn, and yet the standardized achievement test scores go down and
illiteracy rises. Could it be that one
of the key elements we’ve been missing is simply movement?”
By Rae Pica, Movement
Specialist. (Early childhood news. Professional
resource for teachers and parents)
Another
online article that I found on Summons using the Middlesex Library research
tools is:
‘The
Creative Curriculum for Preschool Children’
By
Diane Trister Dodge, Laura J. Colker and Cate Heroman’
Link: Summons Middlesex
University Library E-book download.
In
this article April Kaiser (CCC Teacher) explores the importance of music and
movement in the everyday early years setting. She explains what skills music and movement
can help pupil’s development and how teachers can use music and movement to
benefit their teaching by touching on her own experiences. This article helps
my inquiry as it’s evidence from a teachers point of view:
The Importance of Music
and Movement
by April Kaiser (CCC
Teacher)
Children naturally love music! Whether it’s soft and
soothing or a lively tune, children feel it both physically and emotionally.
Throughout the early years, children are learning to do
new things with their bodies. Young children are also learning that movement
can communicate messages and represent actions. Young children are able to
perform and recognize pantomimed actions such as ironing, stirring, swimming,
or playing the piano.
Most children usually are quite at home with movement.
They begin to learn about the world by acting on objects and people, and they
“think with their bodies” well before they think with words. This is why body
movement is not only fun for children but also a good opportunity for them to
solve problems. When you ask questions that call for verbal responses (“Can you
think of some other ways that Pooh could get up to the honey tree?” or “What
did we do to make applesauce yesterday?”), some children may have difficulty
responding in words. But when questions call for movement (“What are some ways
you can think of to get from one side of the mat to the other?”), children
aren’t limited by their verbal abilities. Movement problem challenge children
in different ways and help teachers/parents learn about the problem solving and
creative abilities of less verbal children.
Singing or chanting can help make routine activities and
transitions, such as gathering children into a circle or group activity,
smoother and more enjoyable. And music helps to set a mood. Quiet, soothing
music calms and relaxes children, while a lively marching tune rouses them for
energetic clean‐up
time. Music and movement are also social activities that help children feel
part of the group.
As children grow in their appreciation of the beauty of
music and dance, they acquire a gift that will bring them great pleasure. Music
brings another dimension of beauty into our lives.
Music and movement benefit a child’s development in many
ways.
Here are skills that music and movement can help develop:
1. Participating in a group
2. Social skills
3. Express emotions
4. Enhance self‐concept
by sharing music and dance of each other’s culture
5. Refine listening skills‐noticing changes in tempo or pitch
6. Awareness of movement and body positions
7. Creativity and imagination
8. Learn new words and concepts
9. Explore cause and effect
10. Develop large motor skills
11. Improve balance, coordination, and rhythm through dance
and movement activities
12. Improve small motor skills‐learning finger plays and playing
musical instruments.
Sources: The Creative Curriculum for Preschool
Children by Diane Trister Dodge, Laura J.Colker and Cate Hreoman. (Middlesex
University Library E-book download.)
Having
looked and literature research and articles online I looked at information
sources within my own work place and evidence I use on a daily basis. The
observations I carry out on pupils follow the early years curriculum and within
them they have areas that concentrate on reaching music and movement progress
targets see examples below: